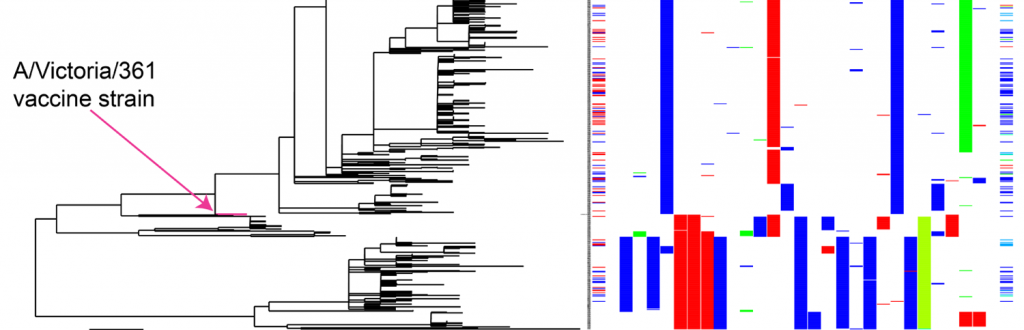
Influenza vaccines usually reduce the risk of acquiring influenza, but the reasons for their imperfect efficacy are not always clear. Are influenza infections in vaccinated individuals caused by antigenically diverged viruses that escape vaccine-induced antibodies, or is something more complicated going on?
Microfluidic devices for microbial sequencing
Skin colonization with methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) is a major risk factor for invasive MRSA infections.
Enterococcus spread in hospitals
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality, particularly in patients who are hospitalized or have weakened immune systems.
Staphylococcus aureus carriage and decolonization
Skin colonization with methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) is a major risk factor for invasive MRSA infections. While decolonization protocols reduce rates of carriage, they are not always successful.
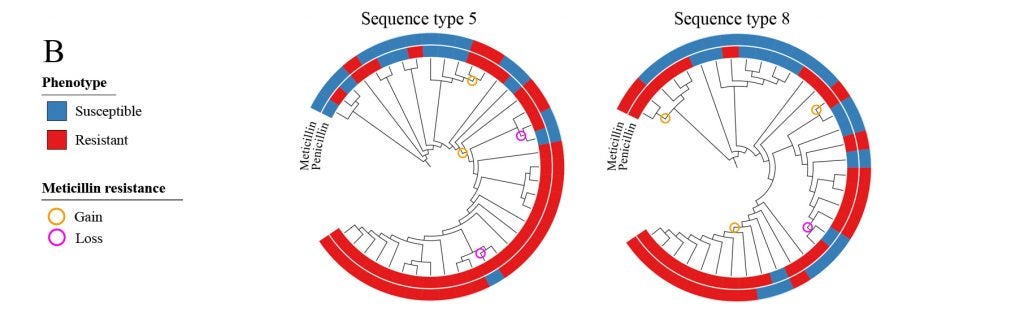
Staphylococcus aureus antibiotic resistance
Soon after the introduction of penicillin in the early 1940s, penicillin-resistant S. aureus emerged clinically. Now, more than 70 years later, penicillin susceptible S. aureus still cause clinical infections.
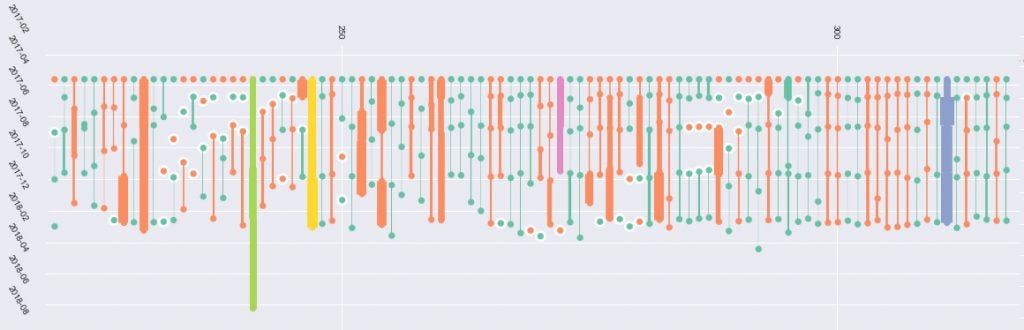
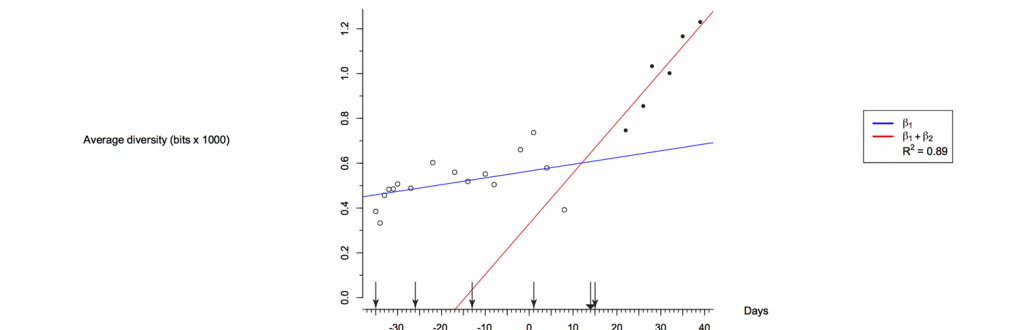
Within-host viral diversity in acute infections
RNA viruses have an error prone RNA dependent RNA polymerase, large population sizes, and rapid turnover, leading to the hypothesis that RNA viruses evolve over the course of an individual infection under the selective pressure of host immune responses.
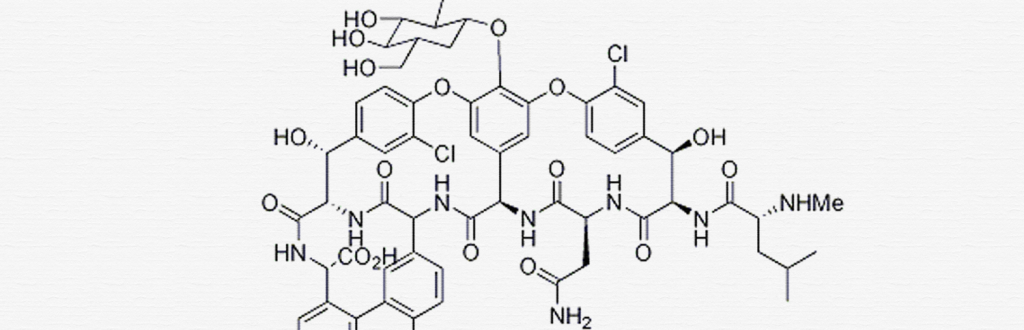
Antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae
N. gonorrhoeae (also known as the gonococcus, the bacterial agent that causes the sexually transmitted disease gonorrhea) is responsible for an estimated 820,000 infections a year in the US and over 106 million a year globally.